How To Design A Product And Get It Made
(This is a sponsored commodity.) What is a product? Until recently, the term was used simply in relation to something material and often found in a retail store. Nowadays, it is coming to mean digital products as well. Apps and websites are mod products.
When information technology comes to building smashing products, design is the most important "characteristic." Nosotros've moved into the stage where production design dominates — information technology's what sets companies apart and gives a real border over competitors.
Whether you're a designer, developer, product manager, program managing director, marketing manager or projection managing director, it's essential to understand (and have a reference guide to) the product development process in social club to create your best piece of work.
In this article, I'll focus on the principal principles and approaches that will assist you to design neat products. I'll start with global things (like what product design is all about) and work down to the individual phases of production design (such as enquiry, ideation, testing and validation).
What Is Product Blueprint?
Product design is the procedure of identifying a market opportunity, conspicuously defining the problem, developing a proper solution for that trouble and validating the solution with real users.
Design Thinking Every bit The Foundation For The Design Procedure
Design thinking is a method for the practical resolution of problems. Originally coined by David Kelley and Tim Chocolate-brown of IDEO, design thinking has go a popular arroyo to creating products. This approach encapsulates methods and ideas of human-centered design into a single unified concept. According to Tim Brown:
Pattern thinking is a human-centered arroyo to innovation that draws from the designer's toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of engineering and the requirements for business organization success.
Skillful designers have ever applied design thinking to product blueprint (whether physical or digital) because information technology's focused on end-to-end production development, and non merely the "design phase" function.
More after jump! Continue reading below ↓

When thinking about products or features, designers should understand the business objectives and be able to respond the following questions first:
- What problem are we solving?
- Who has this problem?
- What do we want to achieve?
Answering these questions helps designers understand the user experience of a product as a whole, not purely the interaction (feel) or visual (look) role of pattern. Simply afterward answering these questions does it make sense to motion to finding a solution for the trouble.
Finding a solution to a problem includes the post-obit v phases:
- Empathize
Learn almost the people for whom you lot are designing. Conduct research to develop a deeper agreement of your users. - Define
Create a point of view that is based on user needs and insights. - Ideate
Brainstorm and come up with as many creative solutions as possible. Generate a range of potential solutions by giving yourself and your team total freedom. - Prototype
Build a prototype (or series of prototypes) to exam your hypothesis. Creating a prototype lets designer see if they're on the correct track, and it oftentimes sparks unlike ideas that you wouldn't have come up with otherwise. - Examination
Render to your users for feedback.

Design Process
Now, with an understanding of what design thinking is, it's fourth dimension to define the pattern process. The design process is a series of steps that product teams follow during the formulation of a product from outset to finish. Having a solid well-structured process is essential for 2 reasons: It helps you to stay focused and helps y'all to stay on schedule.
While it's impossible to provide a universal design process that fits all projects, it's all the same possible to describe a full general flow for designing new products. This flow includes the following steps:
- Defining the production vision
- Product research
- User assay
- Ideation
- Design
- Testing and validation
- Mail-launch activities
1. Define Product Vision And Strategy
Ane of the most important phases of product pattern is actually done earlier the design process even starts. Before you starting time building a product, you lot need to sympathise its context for existence. Information technology'south the time when the product team must define the product vision and production strategy.
Have yous ever worked on a project whose overall goal was not articulate? In which the people involved in the design and evolution only vaguely understood the purpose of the product? Quite often this happens because there is no vision for the product. Unfortunately, this scenario happens all likewise often. In nigh cases, this has negative consequences. Every bit the old Japanese proverb goes, "Vision without action is a daydream. Action without vision is a nightmare."
Every design project needs a product vision that sets the direction and guides the product development squad. Vision captures the essence of the product — the disquisitional information that the product team must know in order to develop and launch a successful product. Vision helps build a common understanding of "what we are trying to build here and why." Vision also helps y'all to define what you are not building. Beingness clear about the boundaries of your solution will help you to stay focused when crafting your product.
Simply vision is only half of the picture. The other half is strategy. Product strategy defines a product'south journeying. Your vision helps you lot define a destination (the target condition) — the ultimate user feel toward which you're aiming. Y'all can plan your route toward the target destination by focusing on exactly what y'all need to build. By setting the goal (the challenge), you tin adjust the management of your production efforts.


Spending fourth dimension and coin on vision cosmos is a worthwhile investment because this phase sets the stage for the success of a production.
Define Value Proffer
Value proposition maps out the key aspects of the product: what it is, who it's for, and when and where it will exist used. Value proposition helps the team and stakeholders build consensus around what the product volition be.
Working Backwards
A uncomplicated technique called "working backwards" adds clarity and definition to the vision of a product. Every bit the proper name suggests, the production squad starts with target users and works its way back until it gets to the minimum set of requirements to satisfy what it is trying to achieve. While working backwards can be applied to any specific product decision, this approach is especially important when developing new products or features.
For a new production, a product team typically starts by writing a future press release announcing the finished production. Such a printing release describes, in a elementary fashion, what the product does and why it exists. As with any other press release, the goal is to explicate to the public what the product (or new characteristic) is and why it matters to them. The press release should enable each team fellow member to envision the future product.
Tips:
- Put the user at the center.
The press release should center on the customer's trouble. When writing a printing release, focus on the value that the product brings to customers. - Read the press release to potential users, and inquire for their feedback.
If the benefits listed in the press release don't audio very interesting or exciting to the target audience, and so perhaps they shouldn't be built. Instead, the team should keep iterating on the press release until they've come up up with a proper set of benefits. - Trim the fat.
A press release isn't a product specification. If the press release is more a page, it is probably also long. - Make sure everyone on the squad shares the aforementioned vision.
Y'all need to not merely define a articulate product vision simply also ensure that all team members share it. - Use the press release as a reference during product development.
One time the project moves into evolution, the press release tin be used every bit a reference. The press release can function every bit a n star to guide your team in times of uncertainty.
Define Success Criteria
It's essential to have a clear business organization goal that you want to achieve with the product. If yous don't know at the beginning of the projection what the business goal is and how success volition be measured, then you're headed for trouble. Defining explicit success criteria — such as expected number of sales per month, key operation indicators (KPIs), etc. — during this stage establishes targets for evaluating progress. This likewise helps to constitute a more results-driven process.
Tip: It's worth interviewing stakeholders to define business goals and objectives for the project.
Schedule A Project Outset Coming together
The commencement meeting brings all the key players together to set proper expectations for both the team and stakeholders. Information technology covers a high-level outline of the product's purpose, who is involved in designing and developing the product, how they will work together, and what the stakeholders' expectations are (such as the KPIs and how success of the production should be measured).
2. Product Inquiry
One time the product vision is defined, product inquiry (which naturally includes user and market enquiry) provides the other half of the foundation for great design. To maximize your chances of success, acquit insightful research before making whatever product decisions. Recall that the time spent researching is never time wasted.
Proficient research informs your product, and the fact that information technology comes early in the blueprint process will relieve you lot a lot of resources (time and money) down the road (because fewer adjustments volition need to be fabricated). Plus, with solid research, selling your ideas to stakeholders will be a lot easier.
Product research is a broad field of study, and covering all aspects of it in this article would be impossible. For more than data on the topic, brand sure to read "A Comprehensive Guide to UX Enquiry."
Comport User Research
Equally product creators, our responsibilities lie first and foremost with the people who volition apply the products we design. If we don't know our users, how can nosotros create great products for them?
Life's too short to build something nobody wants.— Ash Maurya
Skilful user research is key to designing a great user experience. Conducting user research enables you to sympathize what your users actually demand. What it comes to product research, researchers take a few dissimilar techniques to choose from.
Users Interviews
Gathering information through directly dialog is a well-known user research technique that tin give the researcher rich information about users. This technique can help the researcher assess user needs and feelings both before a product is designed and long afterwards it's released. Interviews are typically conducted past one interviewer speaking to one user at a time for 30 minutes to an hour. After the interviews are done, it's important to synthesize the data to identify insights in the course of patterns.
Tips:
- Endeavor to comport interviews in person.
If you have a option, in-person interviews are better than remote ones (via phone or web-based video). In-person interviews are preferable because they provide much more behavioral data than remote ones. You'll proceeds additional insights by observing body linguistic communication and listening for exact cues (tone, inflection, etc.). - Plan your questions.
All questions you lot ask during the interview should exist selected co-ordinate to the learning goal. A wrong fix of questions tin not only nullify the benefits of the interview session, but as well lead production development down the wrong path. - Find an experienced interviewer.
A skilled interviewer makes users feel comfortable by asking questions in a neutral manner and knowing when and how to ask for more details.
Online Surveys
Surveys and questionnaires enable the researcher to get a larger volume of responses, which can open up upwards the opportunity for more detailed analysis. While online surveys are commonly used for quantitative research, they also tin can be used for qualitative enquiry. Information technology's possible to gather qualitative data by asking open-ended questions (for case, "What motivates you to make a purchase?" or "How practice you experience when you need to render the item you purchased from us?"). The answers to such questions volition be very individualized and in general cannot be used for quantitative assay.
Online surveys can be relatively inexpensive to run. The downside of this method is that at that place's no direct interaction with respondents, and, thus, it's impossible to swoop more deeply into answers provided by them.

Tips:
- Go on it short.
Don't forget that every extra question reduces your response rate. If the survey is too long, you may find that yous don't get equally many responses as you'd like. Amend to send a few brusk surveys than to put everything you want to know into one long survey. - Open-concluded versus close-ended questions.
Asking open-ended questions is the all-time approach, just it'due south like shooting fish in a barrel to get stuck in information analysis because every user respond requires researcher time for assay. Plus, users quickly tire of answering open-ended questions, which usually crave a lot of reading and typing.
Contextual Enquiry
Contextual inquiry is a diversity of field written report in which the researcher observes people in their natural environment and studies them as they go almost their everyday tasks. This method helps researchers obtain data virtually the context of employ: Users are first asked a set of standard questions, such equally "What is the most frequent task you typically do?," then they are observed and questioned while they work in their own surroundings. The goal of contextual inquiry is to gather plenty observations that yous can truly begin to empathize with your users and their perspectives.

Tips:
-
Don't just listen to users; observe their behavior.
What people say can be different from what people do. Every bit much equally possible, detect what users do to attain their tasks. -
Minimize interference.
When studying the natural employ of a product, the goal is to minimize interference from the study in order to understand beliefs as shut to reality every bit possible.
Conduct Market Research
You cannot ignore competitors if you desire to build a great product. To be competitive, y'all need to know what products are available on the market and how they perform. That'due south why conducting market research is a crucial component of the product design procedure. Your ultimate goal should be to design a solution that has a competitive reward.
Competitive Enquiry
Competitive inquiry is a comprehensive analysis of competitor products and presentation of the results of the analysis in a comparable way. Research helps product teams sympathise industry standards and identify opportunities for the product in a given market segment.
A competitor is a company that shares your goals and that fights for the same thing that your product team wants. There are two types of competitors:
-
Direct competitors.
Direct competitors are ones whose products compete head to head with your value suggestion (offering the same, or very similar, value proffer to your current or future users). -
Indirect competitors.
Indirect competitors are those whose products target your customer base without offering the exact same value suggestion. For instance, an indirect competitor's chief product or service might not capture your value proposition, merely their secondary production definitely does.
The product team should consider both types of competitors because they'll impact the overall success of the product. As a rule of thumb, shoot for identifying the top three straight competitors and obtaining the same number of indirect competitors.

Tips:
-
Starting time list competitors earlier doing competitive enquiry.
Virtually likely y'all will begin to learn about competitors mode earlier you bear competitive research. For example, during user interviews, users might share names of products that they recollect are like to the one you're proposing. During stakeholder interviews, the product owners will certainly give you a few names of products they meet as competitors. It's worth creating a spreadsheet that will be used to collect the names of competitors right at the starting time of the projection, and try to fill up it as you exercise product research. Add together new names to the list so that y'all don't forget them. -
Utilize a cloud-based tool for competitive research.
Tools such every bit Google Spreadsheet make information technology easier to share the latest upwards-to-date research information with a larger grouping of people (both teammates and stakeholders) and ensure that anybody is on the same page.
Consider reading Conducting Competitive Research past Jaime Levy for more tips on competitive audits.
3. User Analysis
After research, the product team must brand sense of the data it's collected. The aim of the assay phase is to draw insights from the data collected during the production research stage. Capturing, organizing and making inferences about what users want, recall or need tin can assistance UX designers brainstorm to understand why they desire, recall or need that.
Modeling the Users and Their Environments
Personas
Based on the production research results, UX designers can identify fundamental user groups and create representative personas. Personas are fictional characters created to represent the dissimilar user types that might use a product in a similar way. The purpose of personas is to create reliable and realistic representations of the key audience segments for reference. Once created, personas help product teams to understand the users' goals in specific contexts, which is particularly useful during ideation.

Tips:
-
Base the persona on real data.
It can be tempting to invent some details about personas to make them attractive. Avoid that temptation. Equally of the data in the persona should be based on the enquiry. If y'all don't have some data, practise enquiry to fill in the gap. -
Avert using existent names or details of research participants or people y'all know.
This can bias the objectivity of your personas. (You lot'll end up focusing on designing for this person, rather than a group of people with similar characteristics.)
If y'all want to read more information on personas, consider reading "Putting Personas to Work in UX Pattern: What They Are and Why They're Important"
Empathy Map
An empathy map is a visualization tool used to articulate what a production team knows about the user. This tool helps a production team build a broader understanding of the "why" backside user needs and wants. Information technology forces product teams to shift their focus from the product they desire to build to the people who will use the product. Every bit a team identifies what they know about the user and and so places this data on a nautical chart, they proceeds a more holistic view of the user's earth and the problem or opportunity space.

Tip:
- Turn your empathy map into a poster.
Information technology'southward possible to create a nice reminder of what is user thinking or feeling by turning the empathy map into a poster. Create a few copies of the map and hang them around the function. This helps to ensure the user remains on people's minds as they piece of work.

iv. Ideation
The ideation phase is a time when squad members brainstorm on a range of creative ideas that accost the project goals. During this phase, information technology's critical not just to generate ideas but also to confirm that the nigh important design assumptions are valid.
Product teams have a lot of techniques for ideation — from sketching, which is very helpful for visualizing what some aspects of the design will await like, to storyboarding, which is used to visualize the overall interactions with a production.
Generate Ideas (How Users Will Interact With a Product)
User Journey Mapping
A user journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. Typically, information technology'due south presented as a serial of steps in which a person interacts with a product.
A user journey can have a wide variety of forms depending on the context and concern goals. In its well-nigh basic class, a user journey is presented as a series of user steps and deportment in a timeline skeleton. Such a layout makes information technology easier for all team members to empathise and follow the user's narrative.
A simple user journey reflects only one possible path during i scenario:

A complex user journey tin can cover experiences occurring at unlike time sessions and scenarios:

Tip:
- Don't make user journeys too complex.
While designing a user journeying it is like shooting fish in a barrel to get caught upward in the multiple routes a user might take. Unfortunately, this often leads to busy user journeys. Focus on creating a unproblematic, linear journey (the platonic way to get users to the given goal).
Scenarios and Storyboards
After you've identified personas, you can write scenarios of interactions. A scenario is a narrative describing a day in the life of a persona, including how a production fits into their life. A storyboard presents the user'southward story in a visual way — similar to a picture show or comic. Information technology can help product designers understand how people collaborate with a product in real life, giving designers a clear sense of what's really important to users.

Tips:
- Build a strong narrative.
The narrative in the story should focus on a goal the character is trying to achieve. All too often, designers jump right into explaining the details of their blueprint earlier explaining the backstory. Avoid this. Your story should be structured and should take an obvious outset, center and cease.

- Blueprint a clear outcome.
Make certain your storyboard leaves the audience with no doubt nearly the consequence of the story. If you're describing an unfavorable situation, terminate with the full weight of the trouble; if you're presenting a solution, stop with the benefits of that solution for your graphic symbol.
You'll detect more tips on how to create storyboards in the article "The Part of Storyboarding in UX Design."
User Stories
A user story is a simple description of something that the user wants to accomplish by using a product. Hither is a template for user stories:

Tip:
- Apply user stories to prevent feature pitter-patter.
Feature creep is the tendency to add more features than a product requires. When designing a product, try to turn down adding any feature without a user story that explains why that particular characteristic matters.
Job Stories
A chore story is a fashion to describe features. Information technology's a clarification of a feature from a jobs-to-be-done perspective. A job story is an effective technique for defining a problem without being prescriptive of a solution.

Tip:
- Define problems worth solving.
At some point, you'll have several jobs (problems) that you desire to create solutions for. Identify which of those problems have the nearly substantial touch on the user experience or your business organisation goals.
Program The Structure Of A Product
Data Architecture
Information architecture (IA) is the structure of a website, app or other production. It enables users to sympathize where they are and where the information they want is in relation to their current position. Information architecture results in the creation of navigation, hierarchies and categorizations. For example, when a UX designer sketches a top-level menu to help users understand where they are on a website, they're practicing information architecture.

Information compages would benefit from the involvement of users in the IA development process. Product teams typically use a technique chosen card sorting for this purpose. Designers ask users to organize items (major features or topics of the product) into groups and assign categories to each grouping. This method helps you find out how users expect to see information grouped on a website or in an app.

Tip:
- Information technology's possible to comport a card-sorting session online.
Online card-sorting tools allow for easier scaling to a higher number of report participants. One of the nearly pop online tools is OptimalSort (which is free for card-sorting studies with upwardly to 10 participants).
Generate Ideas (What Will the User Interface Look Similar)
Sketching
Sketching is the easiest way to visualize ideas. Cartoon by hand is a fast manner to visualize a concept — enabling the designer to visualize a broad range of design solutions before deciding which one to stick with.

Tip:
- Use a stencil when sketching user interfaces.
When you sketch on paper, it can sometimes exist hard to imagine how certain UI chemical element volition look like at a realistic size. Using a stencil, it'due south possible to draw elements for the actual size of the device yous're designing for. This is especially great when you lot demand to understand whether a UI element y'all've just drawn is large enough for interaction.

Wireframing
A wireframe is a visual guide that represents a page'south structure, as well equally its hierarchy and key elements. Wireframes are useful for discussing ideas with squad members and stakeholders, and to help the work of visual designers and developers. Wireframing acts every bit the backbone of the product — designers often use them every bit skeletons for mockups.
Wireframes can be presented in the form of sketches:

Wireframes can also be presented as digital illustrations:

Tips:
-
Keep wireframes elementary, and annotate them.
The aim of a wireframe is to prove the structure of a page's design — all other details come afterwards. When presenting a wireframe to teams, try to include annotations. Annotations help to create context and chop-chop deliver key ideas. -
Don't use wireframes for product testing.
Wireframes are hardly used for production testing. Even though they help designers gather feedback on design during initial enquiry, they don't supplant actual interaction with a product (through an interactive paradigm).
Validate Ideas
There are two types of ideas: good ideas that lead \to product success, and bad ideas that tin atomic number 82 to failure. Of grade, pattern execution is important, simply the thought itself plays a crucial role in the process. A well-executed bad idea is a big waste of fourth dimension and energy. It's critical to reveal bad ideas equally early as possible. So, how do you distinguish a skillful idea from a bad one? A technique called a blueprint dart can assistance you lot with that.
Design Sprint
A design sprint is a five-day blueprint framework for validating ideas and solving challenges. It enables product teams to build a epitome that they tin can put in forepart of users to validate the initial design hypothesis (to see if it solves the problem for the user).
Pattern sprints are a procedure of chop-chop creating a product's future land, exist information technology a website or app, and validating it with a grouping of users, stakeholders, developers and other designers. This whole concept is based on the idea that, by a design team setting a direction and iterating rapidly, information technology'south possible to design a product that presents the maximum value for people who will utilise it.

Tip:
- Don't get stuck with the outset solution that comes to mind.
In most cases, your first ideas won't be practiced enough, because at the early stage of ideation, you lot won't withal take a adept agreement of the problem y'all're trying to solve. Generate as many different designs as possible instead of focusing solely on your first solution.
five. Blueprint
Afterwards the ideation phase, the product team should have a clear understanding of what they want to build. During the design phase, the product squad will brainstorm to create the solution to solve the client'southward trouble and implement concepts.
Prototyping
To deliver a skilful user feel, prototyping must be a part of your blueprint process. A prototype is an experimental model of an idea that enables you to test information technology before building the full solution. A prototype often starts modest, with you designing a few core parts of a product (such equally key user flows) and grows in breadth and depth over multiple iterations as required areas are built out. The finalized version of a paradigm is handed off for evolution.
When it comes to prototyping, efficiency is vital. One of the most efficient prototyping processes is rapid prototyping. The procedure of rapid prototyping can be presented as a wheel with iii stages:
- Prototyping
Creating a solution that can exist reviewed and tested. - Reviewing
Giving your paradigm to users and stakeholders and gathering feedback that helps you understand what'due south working well and what isn't. - Refining
Based on feedback, place areas that need to be refined or antiseptic. The list of refinements will course the scope of work for your next design iteration.

Prototypes range from crude sketches on a slice of newspaper (low-fidelity prototypes) to interactive simulations that look and function similar a real product (loftier-allegiance prototypes). Depending on the stage of the pattern process and the goals of the prototype, yous'll need to select the appropriate prototyping technique. It's crucial to choose the method of prototyping that minimizes work and maximizes learning.
Paper Prototyping
A lot of digital prototyping tools today help us to create prototypes with the least possible amount of effort, but sketching on a paper even so remains the most important tool for any designer. That'due south because sketching allows designers to speedily explore a lot of dissimilar design alternatives without investing much fourth dimension and energy in each one. It forces designers to concentrate on the essence of a product's pattern (what information technology does), rather than its aesthetics (how information technology looks). And what's especially great about sketching is that it opens upward design to everyone — anyone can sketch, and no special tools are required. The fact that anyone can participate in the design procedure makes sketching an ideal tool during brainstorming sessions.

Tip:
- Paper prototyping allows for rapid experimentation.
Unlike user interface elements can exist drawn, cut out, copied to make extras, and so assembled on a new slice of paper. Digital Prototyping With newspaper prototyping, explaining complex interactions in words can be tough. When a designer needs to explicate a complex design detail such as an animation to a developer or wants to run a user enquiry session to validate a design, they normally use a digital interactive prototype.
Digital prototyping is the procedure of creating an interactive blueprint that other people can experience themselves. But a decade ago, in lodge to build a high-fidelity epitome, you lot really had to code the solution using programming language. These days, prototyping tools let not-technical designers to create high-fidelity prototypes that simulate the functionality of a final product in just a few clicks.
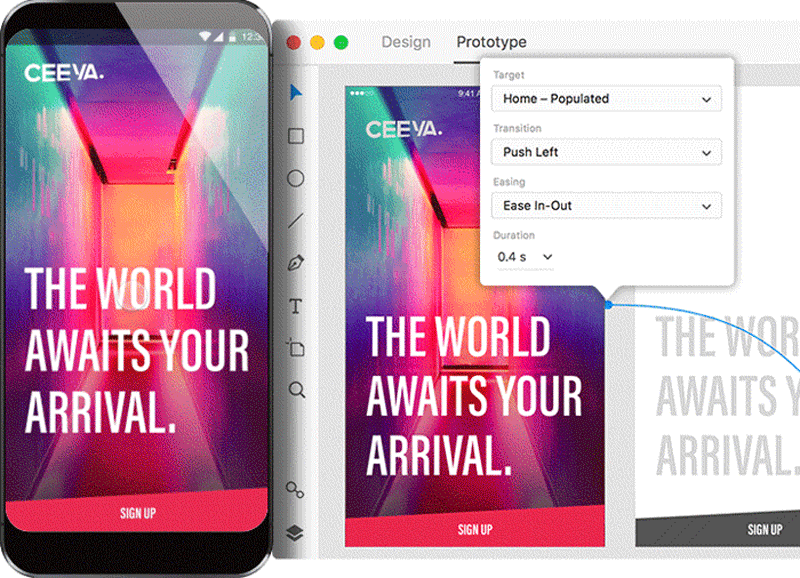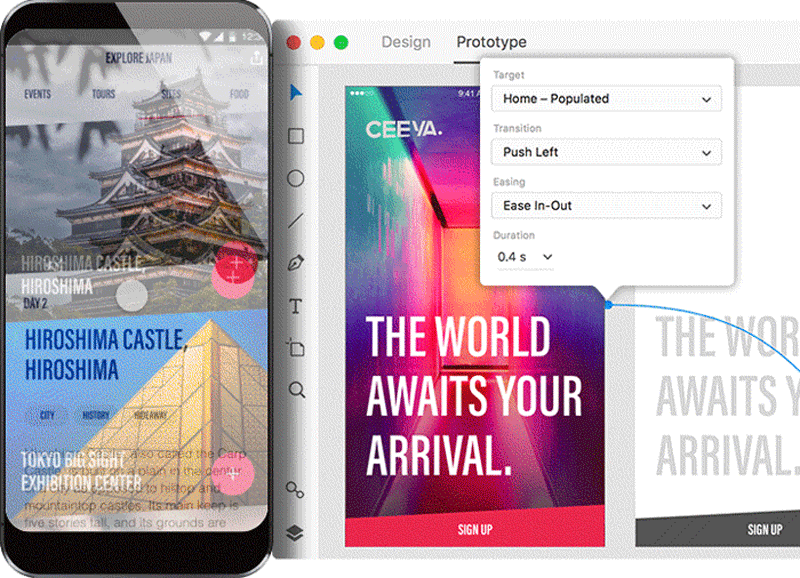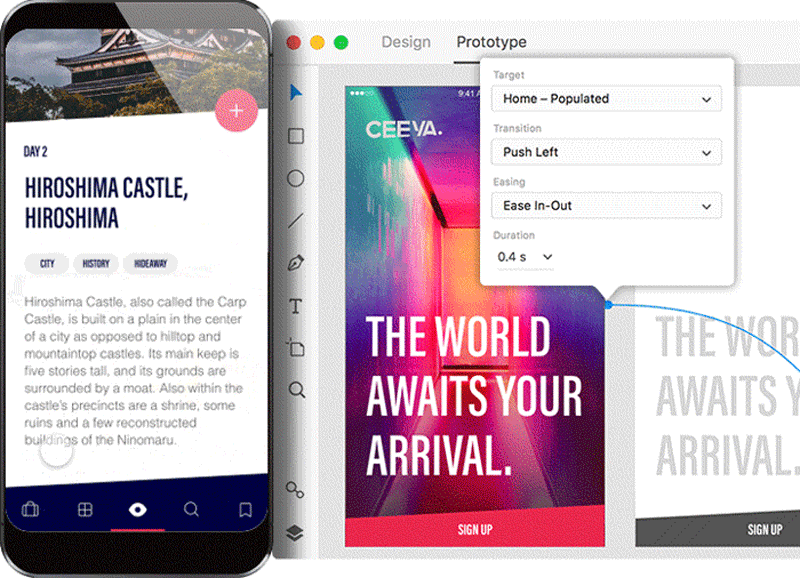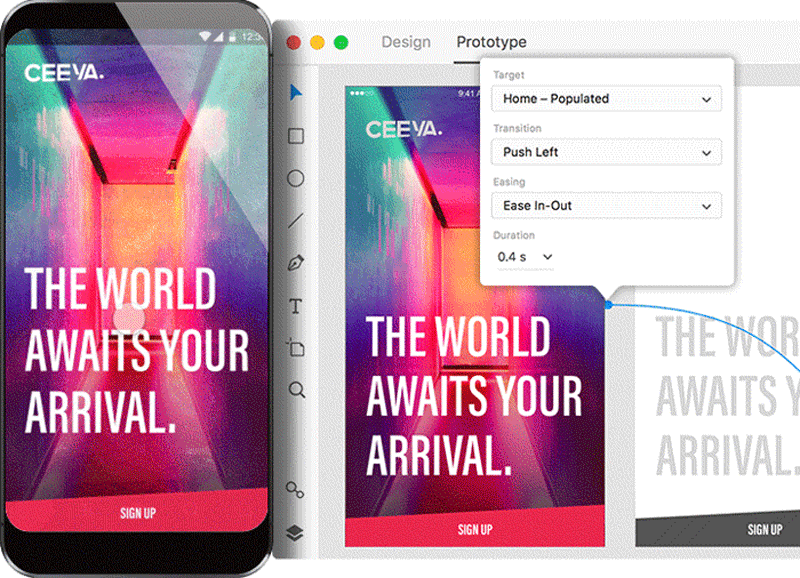
Tips:
-
Avoid dummy text.
Dummy text, like lorem ipsum, should be avoided in early on stages of digital prototyping. Utilize existent content to understand how it affects the overall design. -
Use digital prototypes every bit an up-to-engagement specification for developers.
Prototyping tools such every bit Adobe XD allow you lot to spit out specification documentation in just a few clicks. Information technology's an e'er up-to-engagement specification available to developers.

Design Handoff
At the cease of the prototyping phase, the design will be ready for production. It's the time when the designer hands over the blueprint to a developer for coding. During the developer handoff, a designer must clearly communicate to the programmer how every piece of the blueprint looks and works. Multiple layers of information and detail need to be conveyed, and it's critical for designers and developers to be on the aforementioned page.
Blueprint Specification
Design specs are detailed documents that provide data about a production, such as user interface design details (colors, character styles and measurements) and information (flows, behaviors and functionality). A developer uses this certificate to take the design into product and build the production to the designer'south specifications.

Read "Design Specifications: Speeding Upwards the Design to Evolution Workflow and Improving Productivity" for more than information most design specifications.
six. Testing And Validation
The testing and validation phase helps a product squad ensure the design concept works every bit intended. Product testing is an art in itself. Do it incorrect and you'll learn zero. Do it right and you might get incredible, unexpected insights that might even change your product strategy.
Usually, the validation phase starts when the high-allegiance design is fleshed out. Similar to the product research phase, this stage also varies between projects.
Testing With the Product Squad
It's possible to conduct limited testing for the product using resources you already accept — your team.
Dogfooding
"Eating your own dog nutrient" is a popular technique of testing. In one case the design squad has iterated on the product to the point where information technology's usable, testing it in-house is a great mode to discover the most critical problems.
Tip:
- Do dogfooding to develop empathy amongst your squad.
Testing With Real Users
Usability Testing
According to the Nielsen Norman Group, if yous want to select simply one type of user enquiry for your project, it should be qualitative usability testing. The bones idea behind a usability test is to cheque whether the design of a product works well with the target users. Information technology's relatively easy to test a concept with representative users: Once an interactive version of a product idea is in the hands of real users, a production team volition exist able to meet how the target audience uses the product. The primary goal of this user feel testing method is to place usability issues, collect qualitative information, and determine the participants' overall satisfaction with the product. Gathering and analyzing verbal and non-exact feedback from the user helps a production squad create a better user experience.
Usability testing is often done formally (where a researcher creates a screener, hires participants, has them come into the lab environment, records the session, etc.).

Usability testing tin can likewise be washed informally — in the format of guerrilla testing. With guerrilla testing, a product tester goes to the nearest coffee store, finds participants, asks them to play with a product for 10 minutes, and then gives them a minor care for as a thank you.

Tip:
- You don't demand a lot of examination participants.
According to Jakob Nielsen's enquiry, upwardly to 85% of cadre usability problems can be constitute by observing just five people using the production.
Read the article "Unproblematic Tips to Amend User Testing" for more than data on usability testing.
Diary Study
A diary written report tin can be used to see how users interact with a product over an extended period of time (ranging from a few days to fifty-fifty a month or longer). During this period, study participants are asked to keep a diary and to log specific information nigh their activities. Commonly, the diary includes open up-ended questions such as:
- Where were yous when using the product?
- What tasks did you hope to accomplish?
- Did something frustrate you?
A diary study helps a researcher find answers to questions like:
- What are users' main tasks?
- What are their workflows for completing complex tasks?
The answers provide organic behavioral insights and assistance develop a rich understanding of a participant's context and environment.

Tips:
-
Create clear and detailed instructions for logging.
Be as specific as possible well-nigh what information you lot need participants to log. -
Remind study participants nearly logging.
Prompt participants to fill in their diary (for example, through a daily notification). -
Brand it possible to add screenshots to a diary.
If you use a digital version of a diary, make it possible for participants to upload screenshots. Screenshots are a dainty supplement for user data and volition help you lot with future data analysis.
seven. Post-Launch Activities
Only because a product officially launches doesn't mean the product design is over. In fact, production blueprint is an ongoing process that continues for as long as a product's in apply. The squad will acquire and improve the production.
Understand How Users Interact With The Product
Metrics Assay
You need to know how users are using your product out in the wild — and that's where analytics come in. Numbers provided by an analytics tool (clicks, navigation time, bounce rates, search queries, etc.) tin be used to empathise how people are actually using your product. Metrics can too uncover unexpected behaviors that are not explicit in user tests. Product team must continually rail product performance to encounter if it meets customer satisfaction and if any improvements tin can be made.

Tips:
-
Utilise analytical tools.
Powerful tools such equally Google Analytics and Hotjar tin can be used to understand user behaviors. -
Don't rely solely on analytics.
You can't determine the effectiveness of a product's design based solely on analytics. To validate the analytical insights, you should conduct further hallway tests.
Feedback From Users
The best way to avoid having to rework a product is to inject feedback into the process. Regular user feedback (in the form of online surveys or assay of customer support tickets) should be at the eye of the production design process. This data will drive production refinement.
Tip:
- Don't brand it hard for users to provide feedback.
Don't hibernate the "Leave feedback" option. Make information technology easy and, if possible, rewarding for users to share their feelings and ideas about your product.
Testing Changes In Design
A/B Testing
An A/B test is an appropriate testing method when designers are struggling to cull between two competing elements. This testing method consists of showing ane of two versions randomly to an equal number of users and and then reviewing analytics to see which version accomplished the specific goal more than efficiently.
Tip:
- Get into the habit of A/B testing your design changes.
Knowing that all of your changes volition exist A/B tested will give you lot a tremendous amount of freedom to try new (and potentially risky) things. You won't accept to worry that some change you've made will ruin everything.
Iv Essential Things To Think Near Product Design
ane. The Procedure Should Morph To Fit The Project
When it comes to product design procedure, there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The process employed should exist tailored to fit the project's particular needs, both business organization and functional. Hither are just a few factors that can touch the design procedure:
- customer's needs or preferences;
- how much fourth dimension you lot have (the projection's borderline);
- projection's upkeep (for example, a limited budget won't allow y'all to conduct a lot of interviews).
A process tailored to the capabilities of the business and of users is most constructive. Thus, use what works the all-time for your project, get rid of the rest, and evolve your design process every bit the product evolves.
2. Production Design Is Not A Linear Process
A lot of product teams recollect design is a linear procedure that starts with defining the product and ends with testing. But that supposition is wrong. The phases of the process frequently accept considerable overlap, and ordinarily there's a lot of back and forth. As product teams learn more about the problem being solved, the users and the details of the project (especially the constraints), it may be necessary to revisit some of the research undertaken or effort out new design ideas.
3. Product Design Is A Never-Ending Process
Different more traditional forms of pattern (such as impress design), the design process for digital products isn't a i-time matter, and designers should never assume they'll get everything perfect right from the commencement. Implementation often reveals gaps in the design (for example, bad assumptions virtually product usage, which are hard to predict without shipping the product).
To design successful products, teams demand to adopt a process of continual improvement. Iterative pattern follows the idea that design should exist washed in repeated cycles: It's a process of constantly refining and improving the product based on both qualitative and quantitative feedback data from your users. This is a great opportunity for designers to come across the bigger picture, improve their work based on user feedback and make the product inherently more valuable to users.

4. Product Blueprint Is Based On Communication
While doing bang-up design is ane thing, communicating great design is every bit equally important. The all-time concepts will fail if they don't get blessing from the team and stakeholders. That'southward why the all-time product designers are great communicators.
Determination
The most important matter to remember when designing products is that design is for people. To design cracking products, you must deliver the right features, with the correct user experience for the right people. Thus, define your target audience, then enquiry their issues, and, finally, focus on building a product that solves those problems!
This article is role of the UX blueprint serial sponsored by Adobe. Adobe XD tool is made for a fast and fluid UX pattern process, as it lets you go from idea to paradigm faster. Design, image and share — all in 1 app. You can bank check out more than inspiring projects created with Adobe XD on Behance, and likewise sign up for the Adobe experience blueprint newsletter to stay updated and informed on the latest trends and insights for UX/UI design.
![]() (ra, il)
(ra, il)
How To Design A Product And Get It Made,
Source: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2018/01/comprehensive-guide-product-design/
Posted by: turnerentinver.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Design A Product And Get It Made"
Post a Comment