How Long Does It Take To Get Glasses Made

If you're annihilation like us, you're probably still spending tons of time in forepart of screens due to ongoing social distancing restrictions, and your new habits may stick, even after the restrictions are lifted. Phones, Tv set screens, computers — you proper name it — these gadgets help us get work done and provide bang-up ways to spend our time while we're social distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic, but they also expose the states to a lot more blue light.
For embankment-goers, experts always recommend a healthy coating of sunscreen to protect the pare from those pesky ultraviolet (UV) rays, but sunlight contains more than than just dissentious UV light. In fact, it's fabricated upwardly of cherry-red, green, yellow, blue and orangish light rays, which combine to create "white light" (a.grand.a. sunlight). If you lot haven't sat through a loftier school scientific discipline class in a while, no worries. We'll break down the important stuff about blue calorie-free — without getting too scientific.
What Exactly Is Blue Light?
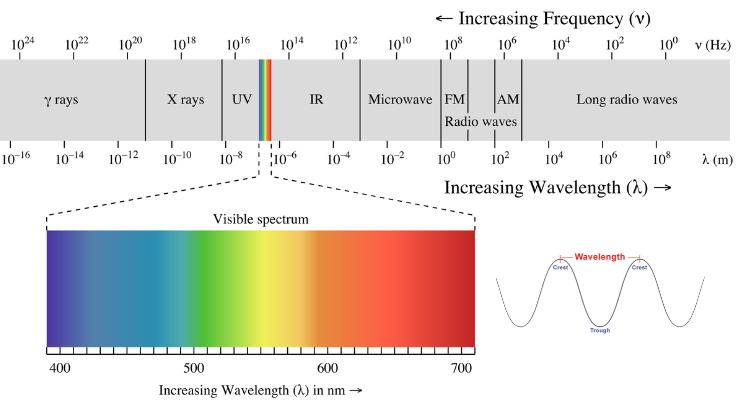
Equally the name suggests, visible low-cal can be seen by the human middle, and each ray reflects a particular color. The color of a given ray depends on the ray'southward wavelength (see the graphic below) — or the distance between successive crests of a wave. (Side annotation: This means that objects get their colors through the wavelengths of the low-cal that are reflected from them. Trust u.s.a. — don't think too hard nearly it. Things get trippy.)

Another important relationship to notation is that of wavelengths and energy: The longer the altitude between waves, the less energy a ray has to offering. Think of it this way — if the wave crests are further apart, they're a flake lazy, but if the crests come in rapid succession, there's a frenzy of energy there. All of this ways rays on the red finish of the visible calorie-free spectrum have longer wavelengths and less energy, whereas rays on the blue stop have shorter wavelengths and more energy.
UV rays, which aren't on the visible light spectrum at all, surpass blue calorie-free in terms of how much free energy they comprise. That incredible corporeality of energy is how those rays are able to create a physical change, like tanning (or called-for) your pare. In moderation ultraviolet radiation tin can be skilful for u.s.a. (think vitamin D), only, on the other hand, it tin besides produce some devastating effects (call back sunburn and snow blindness).
And then, what about blue light — the visible rays that are a few notches below harmful UV rays? Well, approximately ane-third of all visible light is considered high-free energy visible (HEV) blue light. Blue light is literally why the sky appears blue. These rays besprinkle more than easily than other visible rays of light when they strike the atmosphere'south air and water molecules, and all that scattering makes the sky that vibrant bluish color.
There'due south no escaping it, peculiarly because daylight is our main source of blue light, just it's not all bad. Experiencing blue light during the daytime helps regulate your circadian rhythm, makes you more alert, elevates your cognitive office, promotes good recall and is even used in light therapy to care for seasonal affective disorder (SAD). However, human being-made objects — including LED lights and display screens on apartment-screen TVs, computers and smartphones — emit bluish calorie-free besides. Although these devices only emit a fraction of the bluish calorie-free the sun emits, researchers and doctors have yet voiced concerns about patients' excessive screen fourth dimension — and corresponding overexposure to bluish light — in recent years.
Surprisingly, the human eye is pretty neat at protecting the retina from UV rays, just blue light is a dissimilar story. Virtually all of it penetrates the lite-sensitive retina, causing damage that approximates macular degeneration — a status that tin lead to vision loss.
In addition to potentially harming your optics over time, blueish calorie-free tin also lead to eye strain. If you lot have ever ended upwards with a wicked headache after staring intensely at an Excel spreadsheet for hours, you lot're probably familiar with that particular discomfort. When we noted how blueish light contributes to the heaven looking blue, we mentioned that this is truthful because of how blue light scatters. Well, according to All About Vision, this same handful of the blue light that emanates from screens makes for "unfocused visual 'noise' [that] reduces dissimilarity and tin contribute to digital middle strain."
If you don't endure from eye strain due to increased exposure to blue light, these inescapable rays may still accept adverse furnishings on your health. Whatever sort of light — regardless of where it falls on the spectrum — can suppress the human body's ability to release melatonin, the hormone that regulates slumber cycles. However, it's believed that blueish light quashes melatonin secretion even more than other hues do. Researchers at Harvard University compared the effects of blue and green lite exposure and plant that "bluish light suppresses melatonin [secretion] for about twice as long as the green light and shifted circadian rhythms by twice equally much."
How Can You Protect Against Blue Calorie-free?
BluTech, a company that manufactures special bluish light-filtering lenses, reports that "43% of adults accept a job that requires prolonged use of a tablet or computer" — and that's just while those adults are on the clock. Factor in all the time we spend online, texting and marathoning Netflix, and adults spend roughly 12 hours a day looking at screens and taking in blue light. So, how tin can you personally mitigate the harmful effects of prolonged exposure to blue lite?

Well, blueish calorie-free-filtering lenses are condign all the rage. Although not equally ubiquitous equally Away suitcases or Bluish Apron commercials, you may have heard commercials for blue low-cal-filtering specs from Felix Gray or Warby Parker on your favorite podcast or radio talk show. Felix Gray glasses, for example, pride themselves on having a blue light-filtering material embedded within, which the company says will curb center strain, headaches and sleep disruption.
If you're not into wearing a pair of glasses, experts recommend taking screen breaks, both at work and at home; keeping screens clean to reduce glare and eye strain; changing your abrasive white display background to something less vivid; blinking more often; and fugitive screens for at least 30 minutes to an hour before bed because screens stimulate your encephalon. At bedtime, it'south time to trade that fancy blue lite-emitting tablet for a Kindle Paperwhite, or, you know, a skilful old-fashioned book. (Remember those?)
How Long Does It Take To Get Glasses Made,
Source: https://www.ask.com/culture/everything-about-blue-light-glasses?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740004%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex&ueid=8c575564-f736-41a5-abdb-2646238c09d2
Posted by: turnerentinver.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Long Does It Take To Get Glasses Made"
Post a Comment